Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
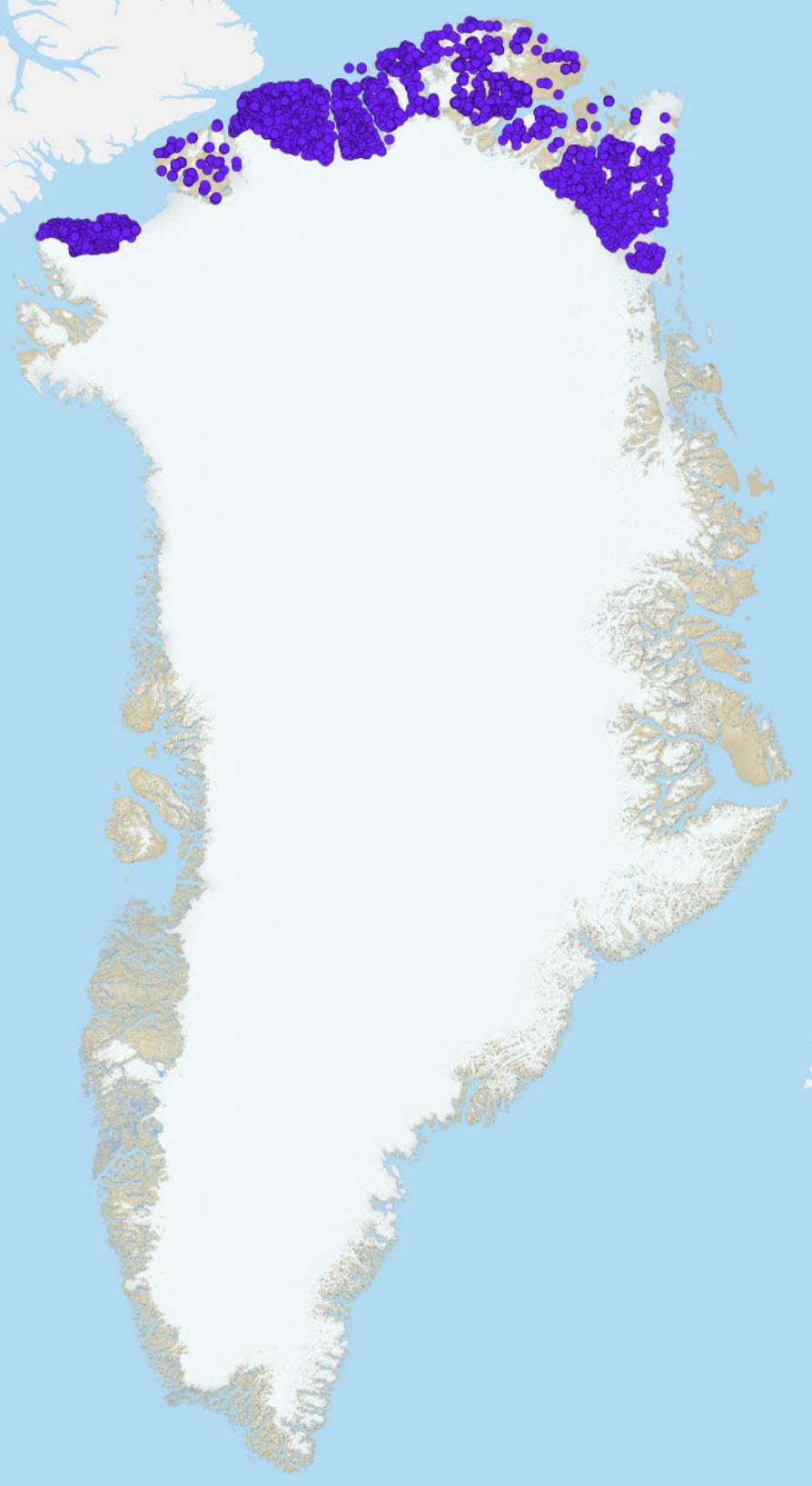
This view presents data selected from the geochemical mapping of North Greenland that are relevant for an evaluation of the potential for zinc mineralisation: CaO, K2O, Ba, Cu, Sr, Zn. The data represent the most reliable analytical values from 2469 stream sediment and 204 soil samples collected and analysed over a period from 1978 to 1999 plus a large number of reanalyses in 2011. The compiled data have been quality controlled and calibrated to eliminate bias between methods and time of analysis as described in Thrane et al., 2011. In the present dataset, all values below lower detection limit are indicated by the digit 0. Sampling The regional geochemical surveys undertaken in North Greenland follows the procedure for stream sediment sampling given in Steenfelt, 1999. Thrane et al., 2011 give more information on sampling campaigns in the area. The sample consists of 500 g sediment collected into paper bags from stream bed and banks, alternatively soil from areas devoid of streams. The sampling density is not consistent throughout the covered area and varies from regular with 1 sample per 30 to 50 km2 to scarce and irregular in other areas. Analyses were made on screened < 0.1 mm or <0.075 mm grain size fractions.
-
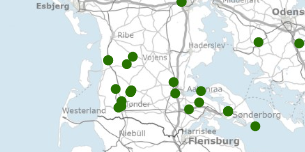
The Samba database among other things contains information about deep wells in the Danish sector, acquired according to the Danish Act on the Use of the Subsoil. That is: exploration, appraisal, delimitation and production wells related to oil/gas. Also wells with other purposes such as: geothermal energy, gas storage, salt production and scientific research. The data sets contains technical, administrative and geological information about the well and about the geophysical measurements undertaken in the well (well logs and reports). Data are submitted by the company to whom the permission has been granted. The database is updated on an ongoing basis.
-
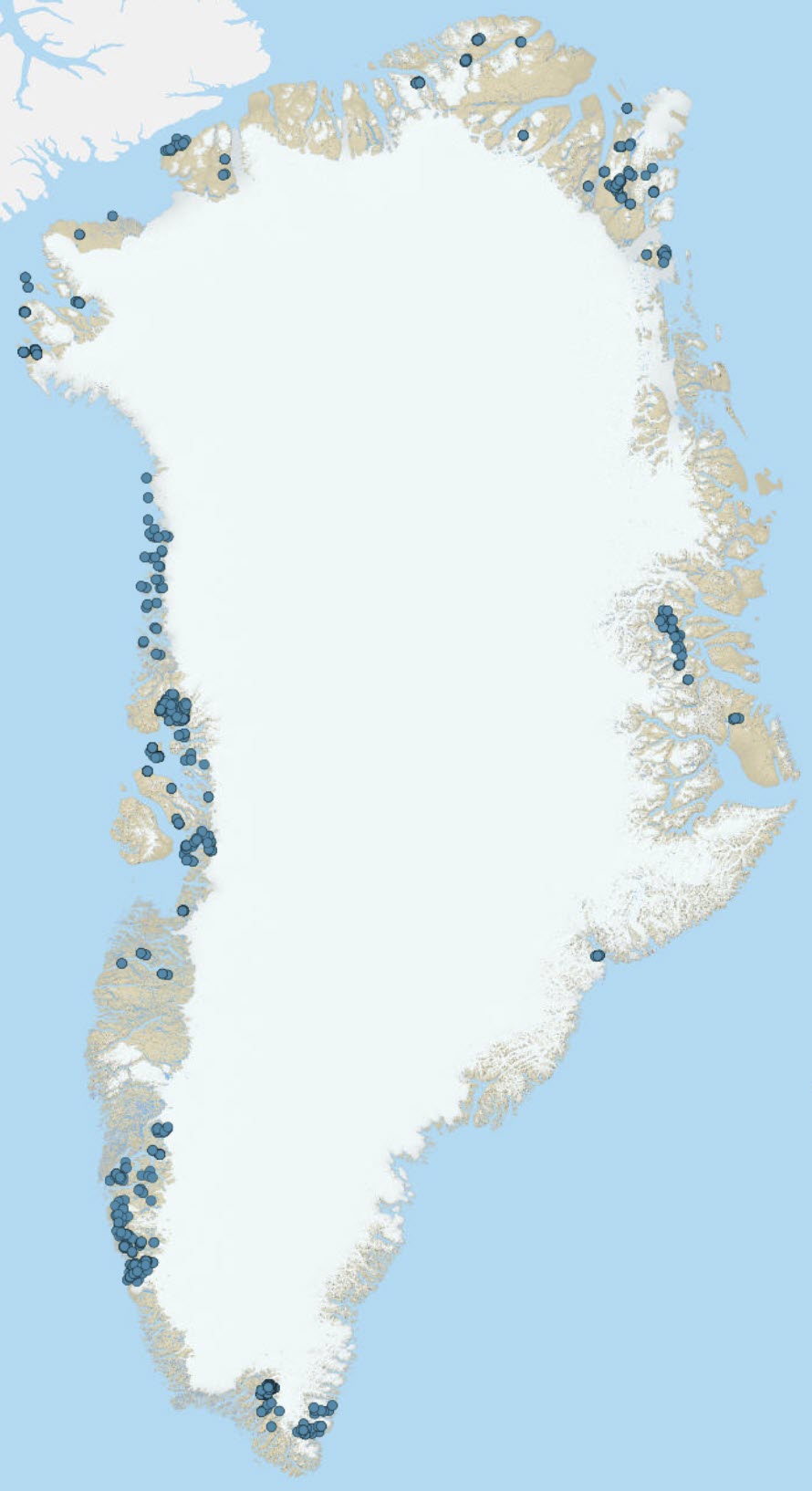
The Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland has previously conducted sampling campaigns of heavy mineral concentrate in Greenland. The sampling methods are described according to their sampling years below. Unfortunately, not all the samples have reported as the campaigns in have not been undertaken on regional scale and therefore fallen under smaller projects or sampled under projects that have had other objects, and not all elements were considered relevant in the reports, translating to that metadata concerning the analyses are missing. All together there are geochemical analyses of 725 heavy mineral concentrate samples. The samples that are mentioned in reports below, are 319 in number, and do not comprise all heavy minerals samples collected the specified years. Samples collected in un-mentioned campaigns do occur in the full list. Use of data that is not mentioned here, needs caution and the quality should be weighed against other data. Years 1982-1986 A regional sampling campaign was conducted between 1982 and 1986, these samples are described in Appel 1989. These samples comprise the analysis batch numbers 10, 36 and 55. Numbers 10, 36 are analysed at Activation Laboratories and 55 analysed at Bondar-Clegg and Co. Ltd., both in Canada. In this campaign 210 samples were collected and are all sampled in the area around Nuuk. Sampling procedure: In the field: The coastal areas were accessed by boat while inland areas were accessed by helicopter. Four litres of coarse gravel and sand were collected and sieved through a 6 mesh of brass. The fines (c. 10 %) was panned and inspected in ultraviolet light and the scheelite grains counted. In the laboratory: The samples were dried and separated by bromoform, the heavy material was weighed and the scheelite grains counted again. A small splitter separated c. 0.5 gram of each sample for analysis of W, Mo, Pb, Cu, Cr, Co, V, Mn, Zr, Ni and Fe. During the years the sampling programme as well as the analysis methods changed. In 1983 the four litres were added up to five. In 1985 the material increased to 5-6 litres (or 10 kg). In 1986 a plastic sieve with 1 mm holes used and filled three times (5-8 kg) for each sample, the volume of fines was measured. C. 10 gram of each sample was analysed by Bondar-Clegg for (Sc, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, As, Se, Rb, Mo, Ag, Cd, Sb, CS, BA, La, Eu, Tb, Yb, Hf, Ta, W, Ir, Au, Th and U) analyses. The reader should note that the analyses below detection limit is given as "0" (zero) and not analysed as "-1" for the samples collected in this campaign (year 1982-1986, i.e. batch numbers 10, 35 and 55). Year 1991 In 1991, 106 streams were sampled for heavy mineral concentrate, in the southern part of the Nuuk area, between 62°30?N and 64°N. Sample procedure was as follows: 5-10 litres of detrital material, < 5 cm, were collected, from 2-5 sub-localities in the stream bed. Wet sieving split the sample in less-than and bigger-than 0.5 mm, and the coarser fraction inspected for economic minerals. The fine fraction was heavy minerals concentrate was produced using a rotary panning device "goldhound" (see Erfurt et al., 1992 for reference). The heavy mineral concentrate was shipped to Denmark and dried and further spilt for analytical purposes. Activation Laboratories, Canada, analysed the samples for 35 elements including gold, with INAA and ICP-ES. Analyses batches are numbered 10 and 36. Unique samples number 103 for these two batches. In additional batch 41, has analysed Pb, Cu, Ni and Zn. Year 2004 The analyses batch no. 193 and 194 have been described in GEUS report 2004/42, and were sampled in 2003 in the Qaanaaq region in North-West Greenland. Six samples were collected in this campaign and sieving of 1.0 mm material on site and a pre-concentrate by panning of the fine fraction. In Copenhagen minerals with > 2.8 g/cm3 density was produced by heavy liquid separation. The rest The remaining 406 samples (analyses batch numbers: 10, 15, 21, 35, 36, 41, 55, 165, 166, 193, 194, 374, 375, 376, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1029, 1030, 1051, 1052, 1077 and 1078) have been analysed in addition to the laboratories mentioned above, at Risø National Laboratory in Denmark. As reports have not been available for writing up these analyses, the description is limited to the analyses. Chances are, however, that sampling procedures are similar to the descriptions above. The analyses below detection limits of the remaining 406 unique samples have not been consistent, but are presented as "0" or as negative values and elements that have not been measured as "0" or empty cells.
-

The digital terrain model of Greenland is constructed on the basis of GEUS's topographic datasets from the official geological maps of Greenland in scale ratio 1:100.000 and 1:500.000. The DEM is created using an interpolation method called Topo to Raster function in ArcGIS Desktop which is primarily supported by contour lines, coastlines and elevation points. The creation of the DEM was divided into in sub-areas based on the map sheet frames from the geological map of Greenland in 1:500.000 scale and assembled as a raster mosaic. The DEM was created with the spatial coordinate reference system WGS 1984 / UTM Zone 24N Complex with a resolution of a 100x100 meter grid. Based on the final DEM, a hillshade efect of the terrain has been constructed.
-
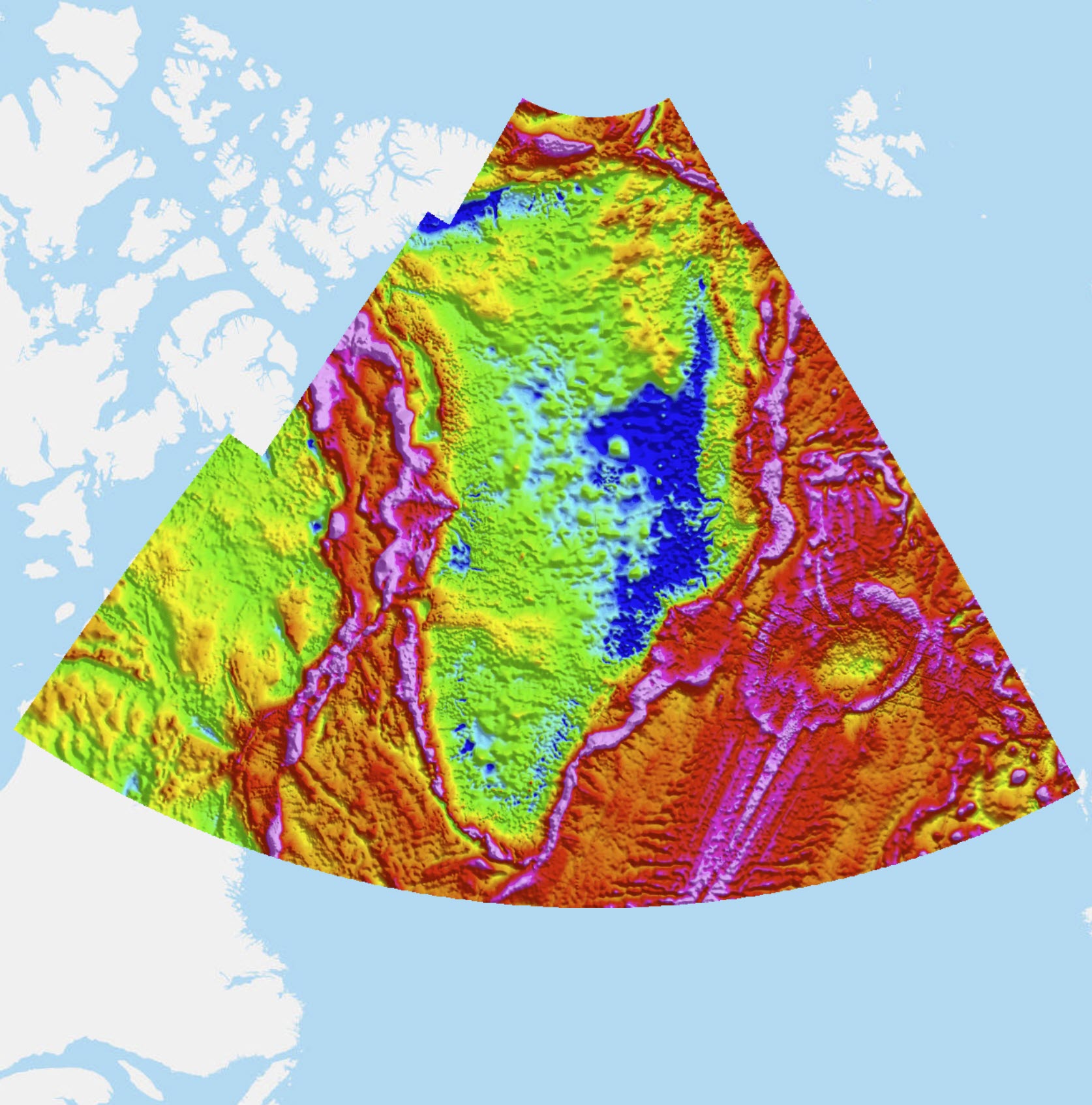
The gravity compilation is based on data stored in the national/Nordic gravity data base at the DTU Space. This data base contains for Greenland data surveyed by DTU Space on behalf of the geodetic survey authorities “Danish Agency for Data Supply and Efficiency” (SDFE) and its predecessor agencies “National Survey and Cadastre” (KMS) and the Geodetic Institute (GI), with some data dating back to the 1950’s. Older data have been rectified into modern gravity datums (absolute gravimetry and IGSN71). The national data contains both surface, airborne and marine data, mainly in the coastal ice-free regions and offshore (Forsberg et al, 2001, Kenyon et al, 2008). Airborne, marine and land data from a number of external data sources are also included in the data base after a QC process, including high-level airborne data from the GAP91/92 campaigns (Brozena et al, 1993) and recent data from NASA OIB (MacGregor et al., 2021) and OMG projects (Fenty et al., 2016). Marine data in the Baffin Bay and Davis Strait and land data from the Geodetic Survey Division, Canada (Veronneau 2010, pers.comm.), and a number of other marine and land data from a large set of contributors have also been included in the compilation, including marine data from Alfred Wegener Institute (Germany), land and marine data from Orkustofnun (Iceland), and a number of released commercial data sources. In areas void of gravity data, satellite-derived altimetry data have been used as fill-in (DTU 15, Andersen et al. 2017). The compiled grids have been based on public domain and some proprietary data sources, and has been computed for the area 58-85°N, 78-7°W on a 0.02°x 0.05° grid, using rigorous downward continuation of airborne data to the terrain surface, with terrain corrections from a detailed digital terrain and ice sheet surface model, and long-wavelength satellite gravity data from GRACE and GOCE satellites (Forsberg and Olesen, 2010). The data are available as a free-air (Faye) anomaly grid as well as a derived terrain-corrected Bouguer anomaly grid (land and ice sheet areas only), computed in GRS80 with density 2.67 g/cm3. The ice sheet Bouguer anomaly data are derived using the ice sheet thickness model of Bamber et al., 2013. The free-air gravity grid (v1) have also have been used as the primary background data also for the latest geoid models of Greenland (GGEOID16).
-
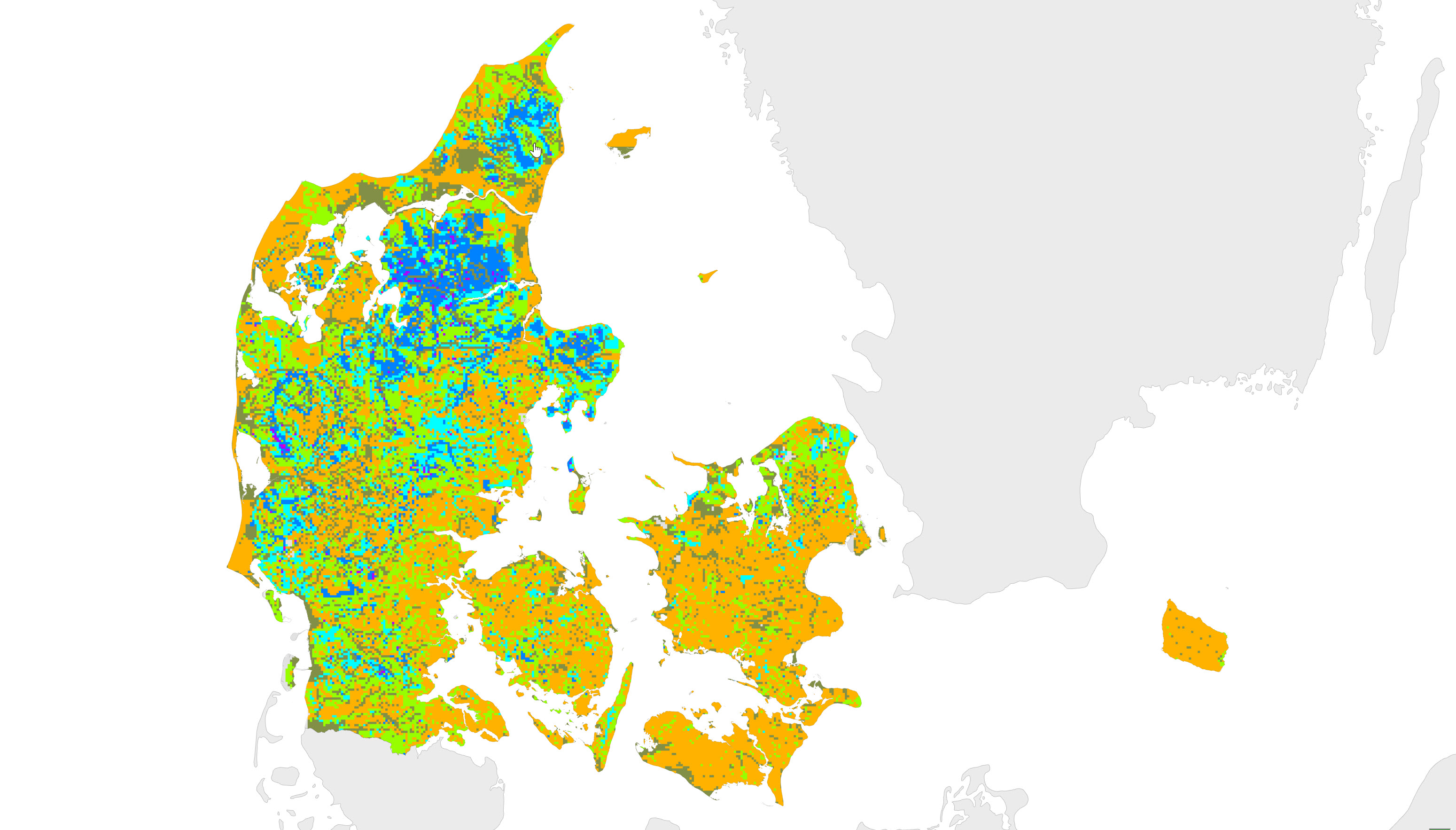
This map is the first national map showing the depth in meters to the uppermost redox interface in sediments of Quaternary age. The redox interface indicates the transition from the oxidized to the reduced geochemical environment in sediments. The redox interface was identified according to the colors of the sediments in 11,999 wells and is shown for 1x1 km grid-cells. For grid-cells with multiple site information, the depth to the redox interface is indicated by an average value. For grid-cells without any field information, the depth of the redox interface was established based on information about 1) geological setting, 2) morphology, 3) depths to redox boundaries at nearby field sites, 4) GEUS surface geology map, 5) topography, and 6) the pre-quaternary surface. The method for this first national redox-map and the data used is described in GEUS report no. 93 (2006) entitled Beregning af nitrat-reduktionsfaktorer for zonen mellem rodzonen og frem til vandløbet. Data og metode for 1.generationskortet (in Danish). The Redox map is also described in Vand og Jord (2011) 18: 37-39 (in Danish).
-
Protected areas in Greenland. The data are converted from the WFS that the ministery of mineral resources (MMR) in Greenland provides. Links are provided in the online resources.
-
The dataset contains outlines of archived historical unpublished geological maps and sections of Greenland mostly created by GGU and GEUS but also some other institutes from 1916 onwards at various scales.
-
applications for different types of activities in Greenland. The data are converted from the WFS that the ministery of mineral resources (MMR) in Greenland provides. Links are provided in the online resources
-
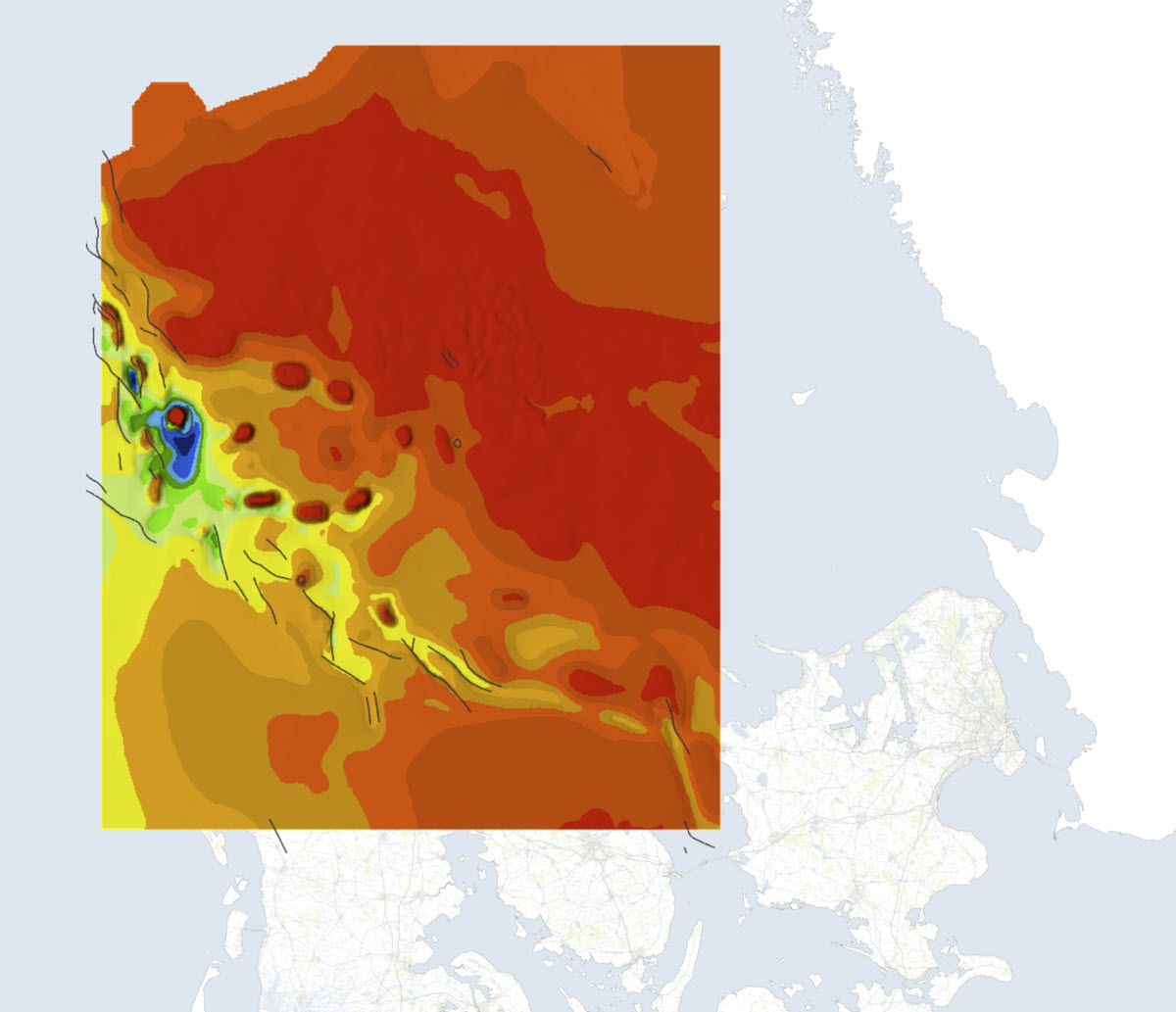
The map is based on selected seismic data up to 2001. The map shows the structural conditions at depth for the 'Top Kalk' surface, from the central to the eastern part of the Danish North Sea. 'Top Kalk' denotes the surface which forms the basis of the Tertiary deposits (except Denmark). The map is described in GEUS Bulletin No. 13. 2007.
 Geus Geonetworks metadata catalogue
Geus Geonetworks metadata catalogue