Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
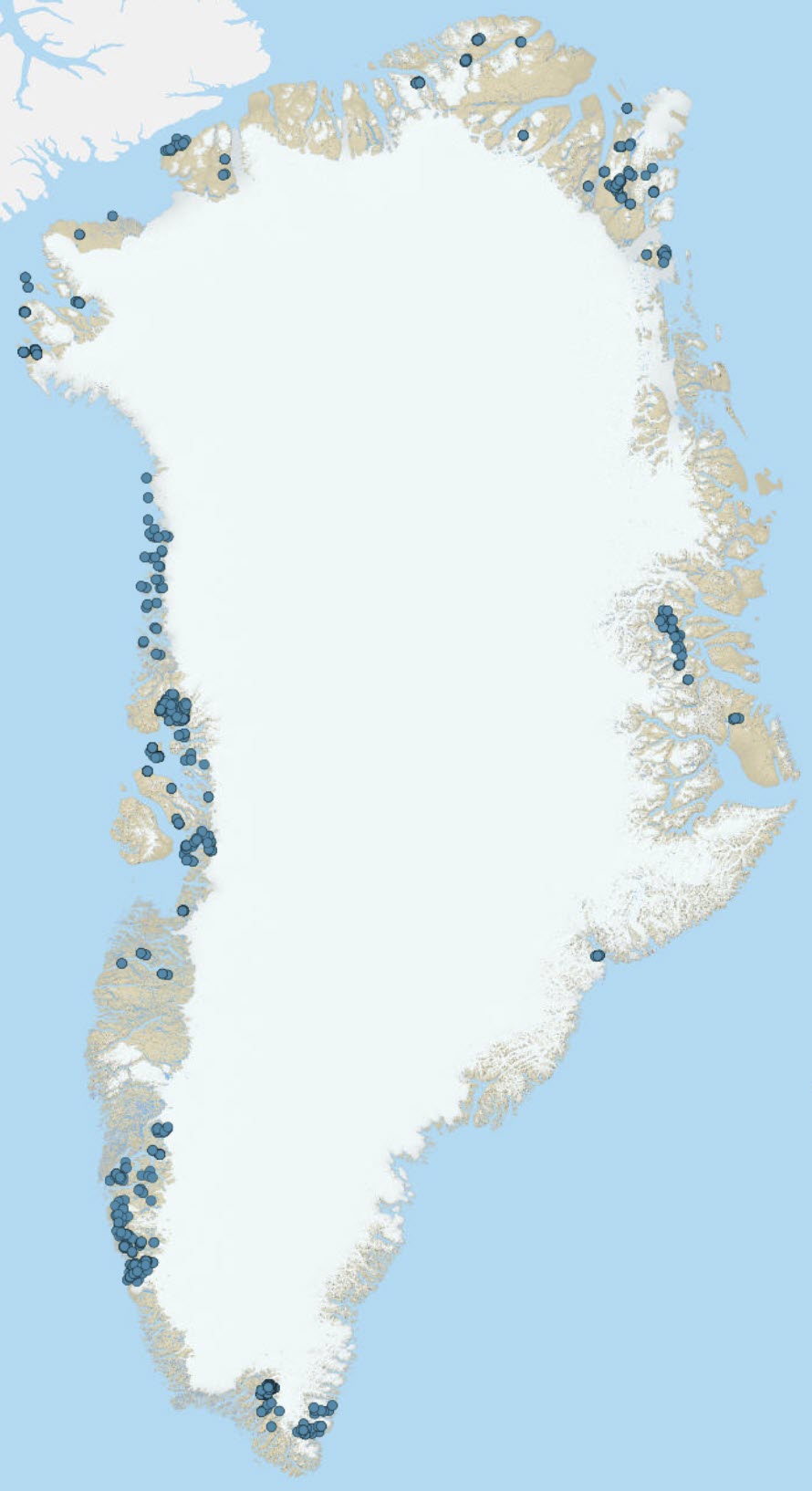
The Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland has previously conducted sampling campaigns of heavy mineral concentrate in Greenland. The sampling methods are described according to their sampling years below. Unfortunately, not all the samples have reported as the campaigns in have not been undertaken on regional scale and therefore fallen under smaller projects or sampled under projects that have had other objects, and not all elements were considered relevant in the reports, translating to that metadata concerning the analyses are missing. All together there are geochemical analyses of 725 heavy mineral concentrate samples. The samples that are mentioned in reports below, are 319 in number, and do not comprise all heavy minerals samples collected the specified years. Samples collected in un-mentioned campaigns do occur in the full list. Use of data that is not mentioned here, needs caution and the quality should be weighed against other data. Years 1982-1986 A regional sampling campaign was conducted between 1982 and 1986, these samples are described in Appel 1989. These samples comprise the analysis batch numbers 10, 36 and 55. Numbers 10, 36 are analysed at Activation Laboratories and 55 analysed at Bondar-Clegg and Co. Ltd., both in Canada. In this campaign 210 samples were collected and are all sampled in the area around Nuuk. Sampling procedure: In the field: The coastal areas were accessed by boat while inland areas were accessed by helicopter. Four litres of coarse gravel and sand were collected and sieved through a 6 mesh of brass. The fines (c. 10 %) was panned and inspected in ultraviolet light and the scheelite grains counted. In the laboratory: The samples were dried and separated by bromoform, the heavy material was weighed and the scheelite grains counted again. A small splitter separated c. 0.5 gram of each sample for analysis of W, Mo, Pb, Cu, Cr, Co, V, Mn, Zr, Ni and Fe. During the years the sampling programme as well as the analysis methods changed. In 1983 the four litres were added up to five. In 1985 the material increased to 5-6 litres (or 10 kg). In 1986 a plastic sieve with 1 mm holes used and filled three times (5-8 kg) for each sample, the volume of fines was measured. C. 10 gram of each sample was analysed by Bondar-Clegg for (Sc, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, As, Se, Rb, Mo, Ag, Cd, Sb, CS, BA, La, Eu, Tb, Yb, Hf, Ta, W, Ir, Au, Th and U) analyses. The reader should note that the analyses below detection limit is given as "0" (zero) and not analysed as "-1" for the samples collected in this campaign (year 1982-1986, i.e. batch numbers 10, 35 and 55). Year 1991 In 1991, 106 streams were sampled for heavy mineral concentrate, in the southern part of the Nuuk area, between 62°30?N and 64°N. Sample procedure was as follows: 5-10 litres of detrital material, < 5 cm, were collected, from 2-5 sub-localities in the stream bed. Wet sieving split the sample in less-than and bigger-than 0.5 mm, and the coarser fraction inspected for economic minerals. The fine fraction was heavy minerals concentrate was produced using a rotary panning device "goldhound" (see Erfurt et al., 1992 for reference). The heavy mineral concentrate was shipped to Denmark and dried and further spilt for analytical purposes. Activation Laboratories, Canada, analysed the samples for 35 elements including gold, with INAA and ICP-ES. Analyses batches are numbered 10 and 36. Unique samples number 103 for these two batches. In additional batch 41, has analysed Pb, Cu, Ni and Zn. Year 2004 The analyses batch no. 193 and 194 have been described in GEUS report 2004/42, and were sampled in 2003 in the Qaanaaq region in North-West Greenland. Six samples were collected in this campaign and sieving of 1.0 mm material on site and a pre-concentrate by panning of the fine fraction. In Copenhagen minerals with > 2.8 g/cm3 density was produced by heavy liquid separation. The rest The remaining 406 samples (analyses batch numbers: 10, 15, 21, 35, 36, 41, 55, 165, 166, 193, 194, 374, 375, 376, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1029, 1030, 1051, 1052, 1077 and 1078) have been analysed in addition to the laboratories mentioned above, at Risø National Laboratory in Denmark. As reports have not been available for writing up these analyses, the description is limited to the analyses. Chances are, however, that sampling procedures are similar to the descriptions above. The analyses below detection limits of the remaining 406 unique samples have not been consistent, but are presented as "0" or as negative values and elements that have not been measured as "0" or empty cells.
-
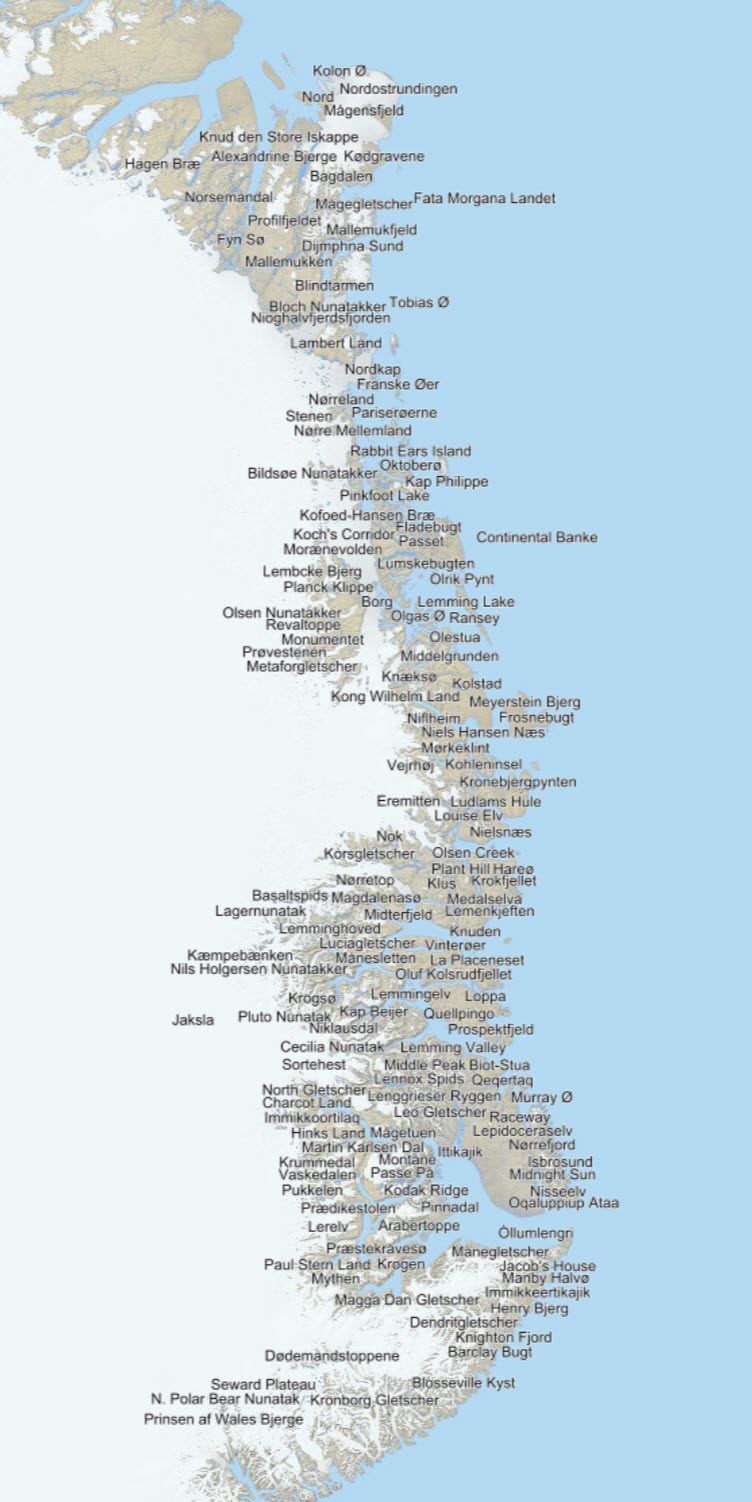
The place names data set is from the book 'Northern East Greenland's research history and place names' by A.K. Higgins, which GEUS published in 2010, with associated maps which have now been converted to web GIS format. Via free text search, you can find the place names with their explanations and their location on the map.
-

The geological maps of Denmark on a scale of 1:400,000 focus on the Danish basin and its geological structures. The map includes areas that extend from the geological age 'Basis Kalk' and the Kalk Gruppen. The 'Basis Kalk' map shows the depth in metres, where 'Basis Kalk' denotes the area that forms the basis for all layers younger than the Early Cretaceous. Over the majority of the mapped area, this surface is level with the base of the Kalk Group, but where the limestone is eroded away, the surface is equal to the base of the Quaternary. The depth to 'Basis Kalk' is calculated as the depth to the base of the deposits younger than Denmark plus the thickness of the Kalk group. The map is published in DGU Map Series no. 29 from 1991, where further information about the mapping can be obtained.
-
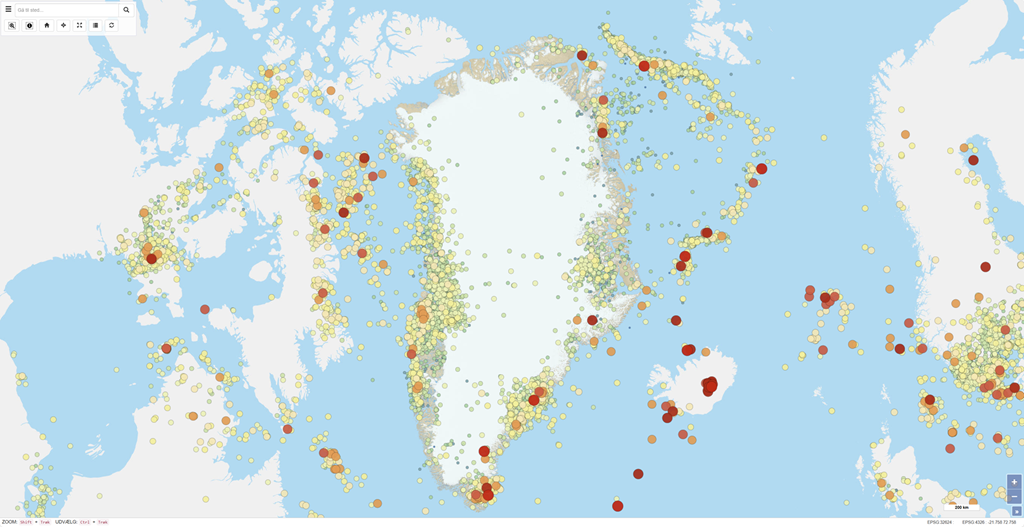
GEUS' Earthquake Portal provides information on all recorded earthquakes in Greenland. The data are extracted from GEUS' earthquake database and are updated daily. As a result, the timing, locations, and magnitudes of events may change as new data are added and existing events are revised. Continuous quality control is carried out, aiming to identify and remove explosions – typically related to military exercises or the removal of old munitions. Therefore, the list may change over time, and some uncertainty may be associated with the determination of epicentres and depths. The portal displays information for each earthquake, including the time of occurrence (year, month, day, hour, minute, second) in Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), the geographical location and depth of the epicentre, and the local magnitude measured on the Richter scale. Earthquake data can be exported from the portal according to the defined zoom level and map extent.
-
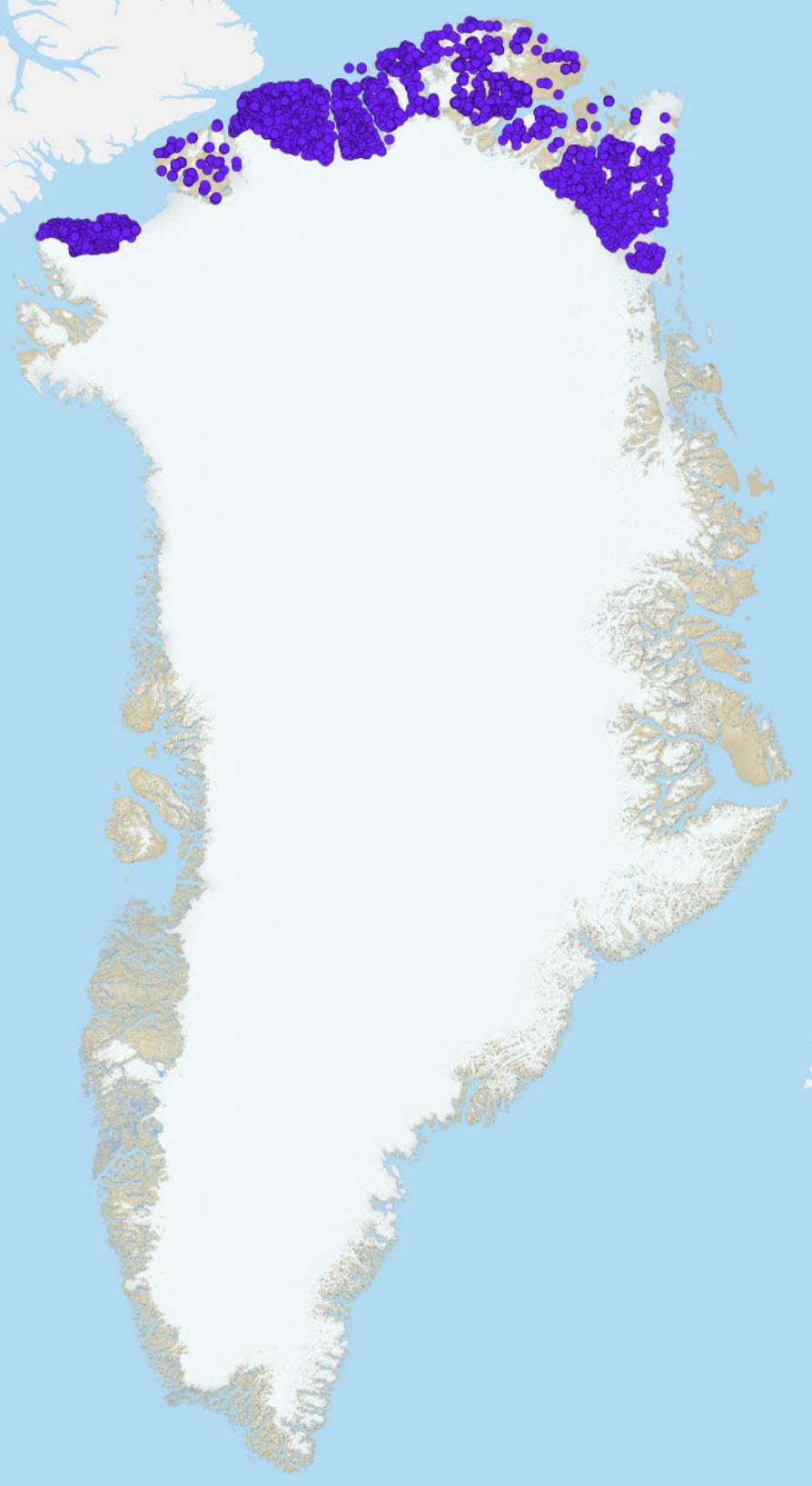
This view presents data selected from the geochemical mapping of North Greenland that are relevant for an evaluation of the potential for zinc mineralisation: CaO, K2O, Ba, Cu, Sr, Zn. The data represent the most reliable analytical values from 2469 stream sediment and 204 soil samples collected and analysed over a period from 1978 to 1999 plus a large number of reanalyses in 2011. The compiled data have been quality controlled and calibrated to eliminate bias between methods and time of analysis as described in Thrane et al., 2011. In the present dataset, all values below lower detection limit are indicated by the digit 0. Sampling The regional geochemical surveys undertaken in North Greenland follows the procedure for stream sediment sampling given in Steenfelt, 1999. Thrane et al., 2011 give more information on sampling campaigns in the area. The sample consists of 500 g sediment collected into paper bags from stream bed and banks, alternatively soil from areas devoid of streams. The sampling density is not consistent throughout the covered area and varies from regular with 1 sample per 30 to 50 km2 to scarce and irregular in other areas. Analyses were made on screened < 0.1 mm or <0.075 mm grain size fractions.
-
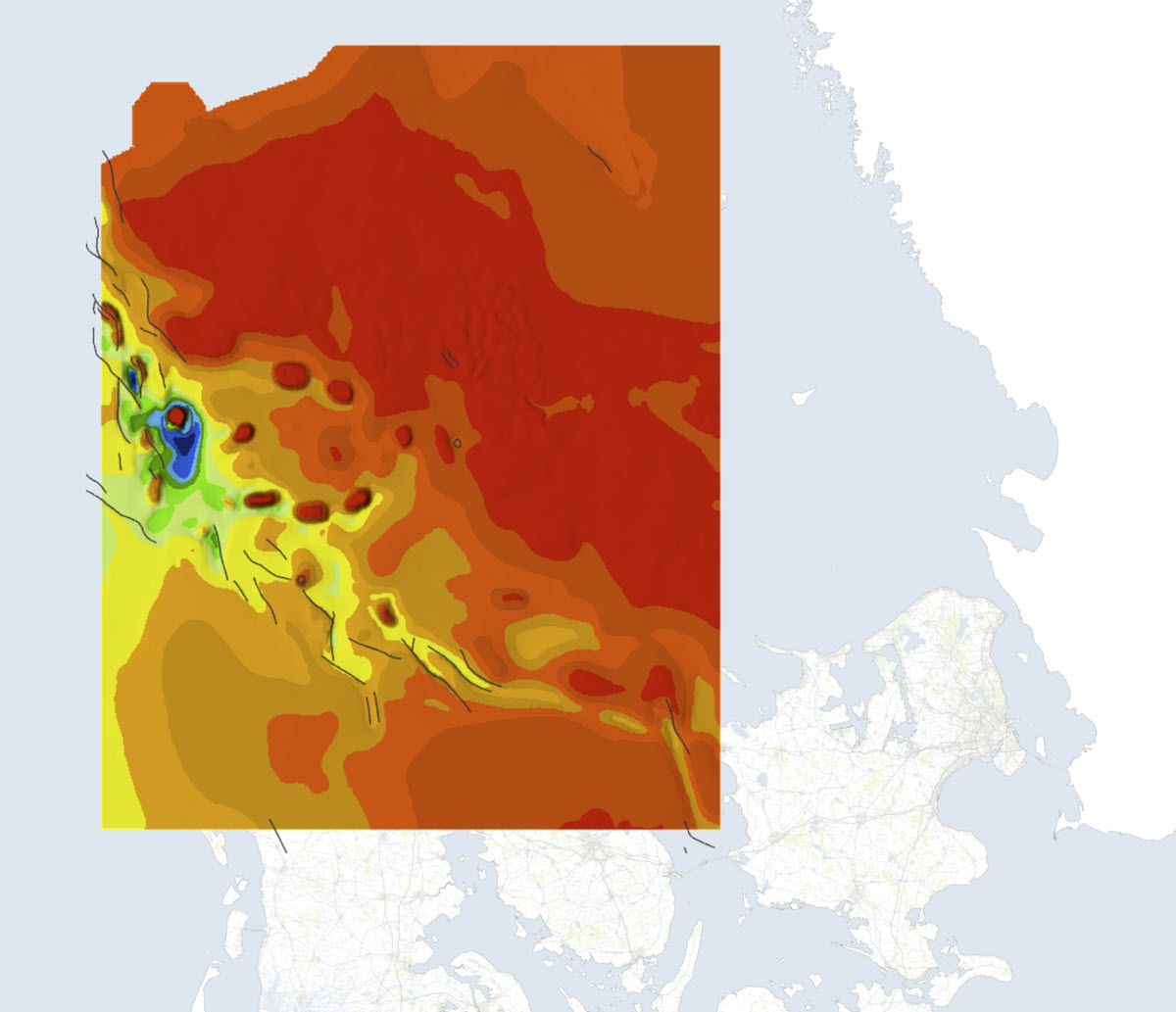
The map is based on selected seismic data up to 2001. The map shows the structural conditions at depth for the 'Top Kalk' surface, from the central to the eastern part of the Danish North Sea. 'Top Kalk' denotes the surface which forms the basis of the Tertiary deposits (except Denmark). The map is described in GEUS Bulletin No. 13. 2007.
-
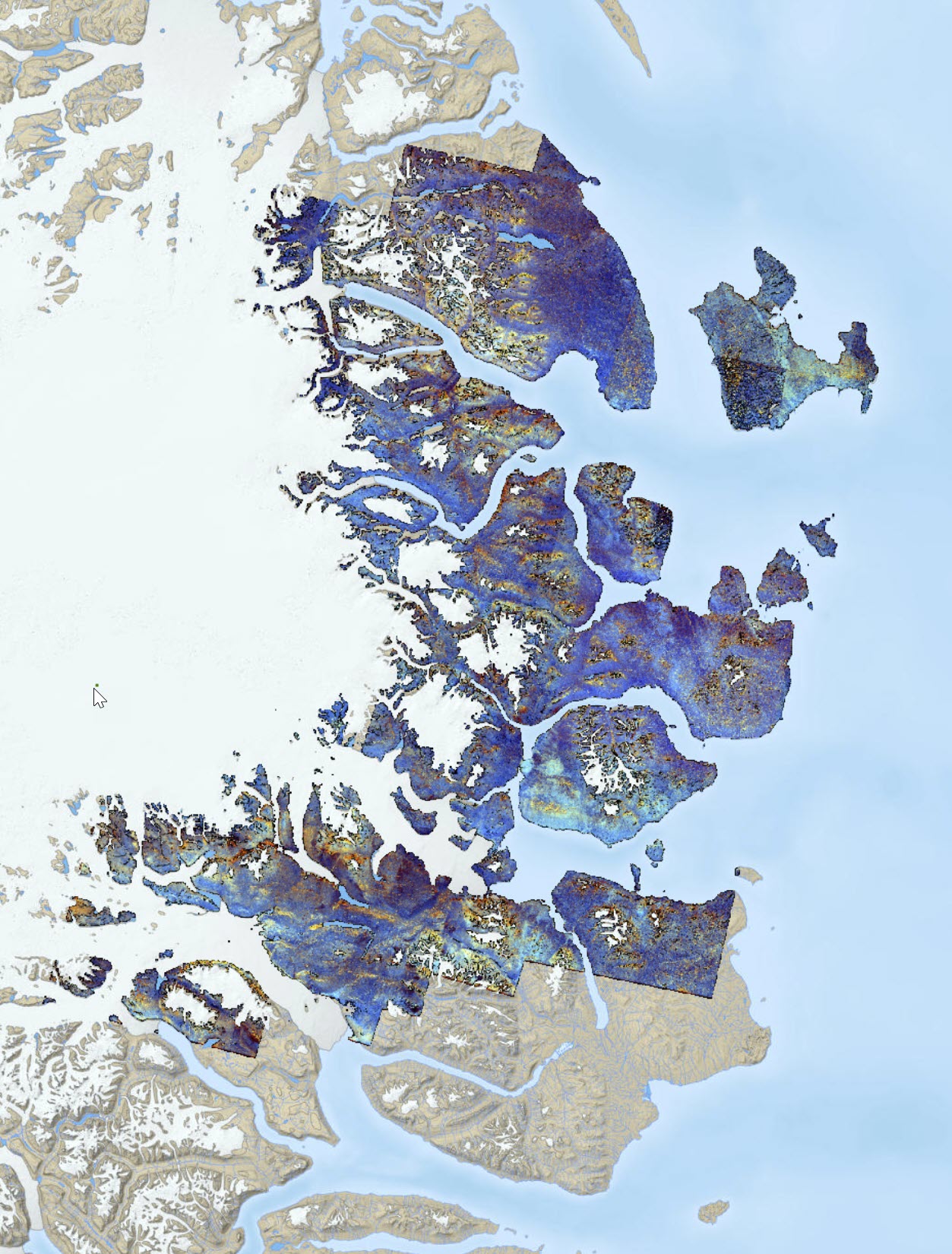

A series of Aster band ratios highlighting mineral distributions. Band ratio color composite images to distinguish variability of lithology in the area. Preprocessing of the Aster scenes encompasses atmospheric, radiometric and topographic corrections before masking non-outcrop pixels and generating the final mosaic. The calibrated radiance data is converted to apparent surface reflectance using a radiative transfer program, Atmospheric and Topographic Correction (ATCOR-3), in rugged terrain mode. The ATCOR rugged terrain mode utilizes a surface elevation model to adjust illumination levels. Calibration and adjusting the apparent surface reflectance values from the ATCOR-3 processing was not feasible due to lack of ground-based reflectance measurements.
-
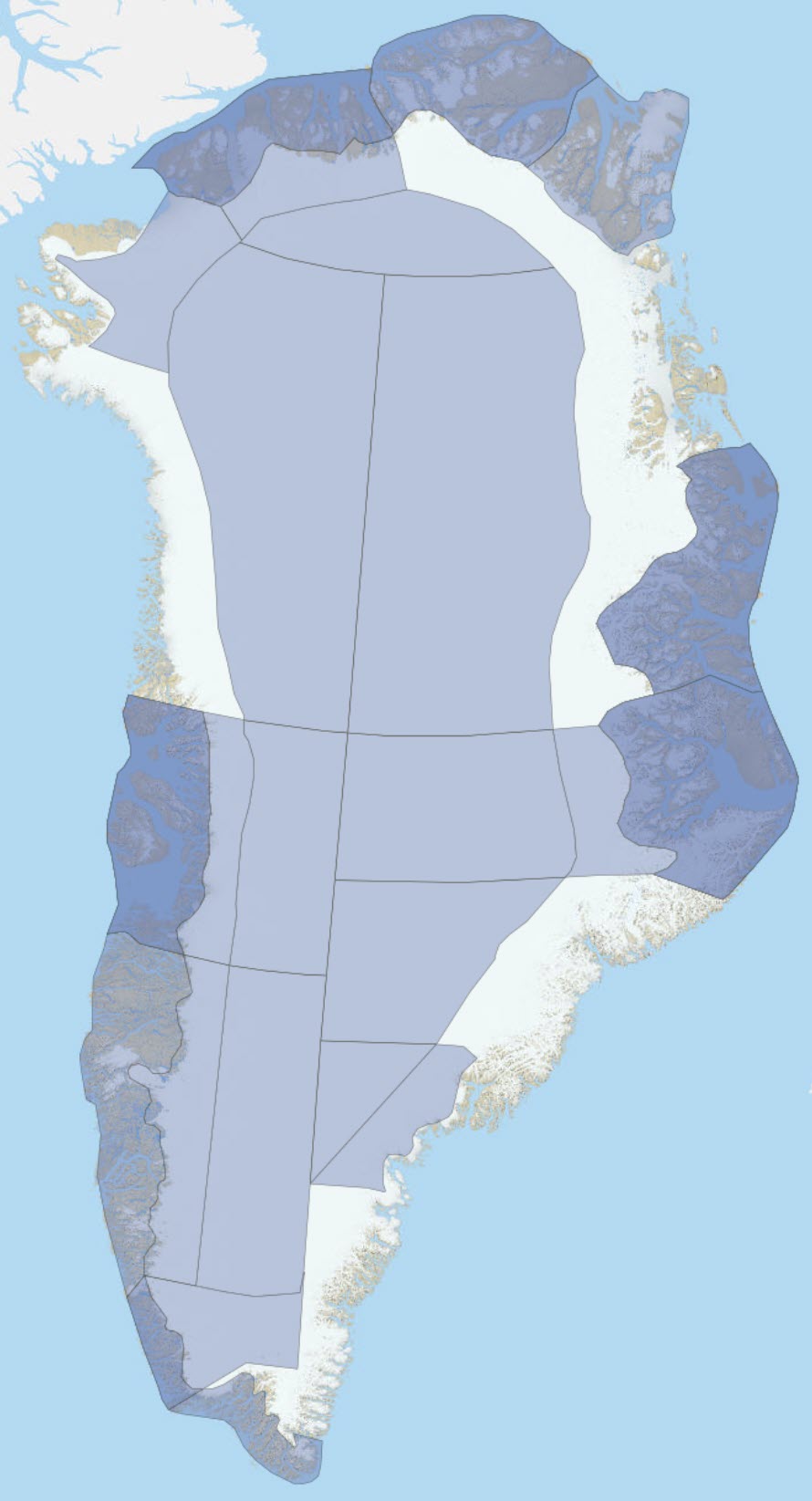
Dataset containing standard polygons for regions of Greenland and specific hand-drawn polygons representing the areas where the study was conducted that is described in the publication. Data can be filtered for publication title, authors, year of publication and the list of attributes contains other reference information including a link to the publication. The publications include GEUS Bulletin (2020 - ), Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin (2004 - 2019), Geology of Greenland Survey Bulletin (1997 - 2002), Bulletin Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse (1948 – 1996) , Danmarks og Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse Rapport, Rapport Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse (1964 – 1996), Open File Series Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse, Mima rapport, Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse Geological Map Descriptions and Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Map Series.
-
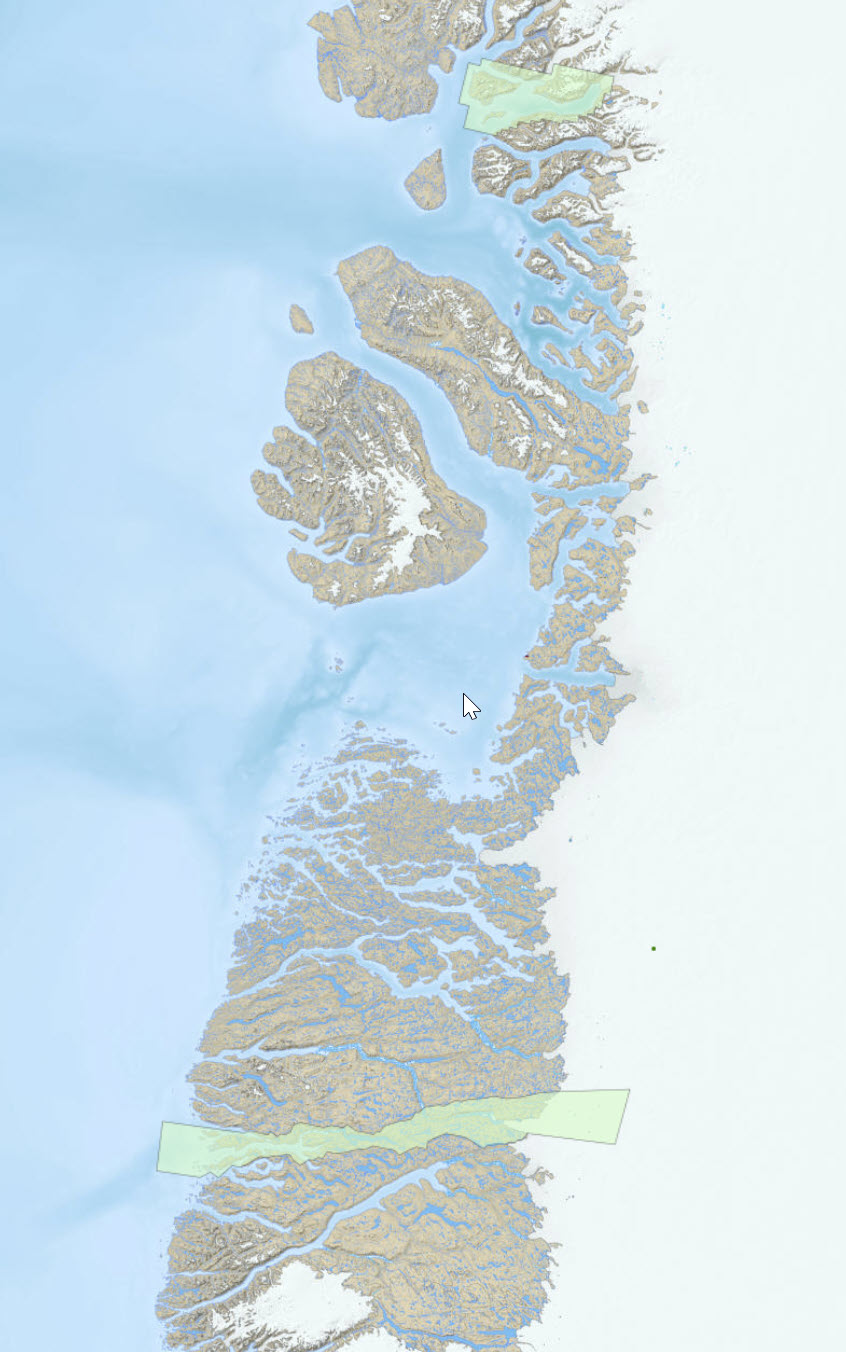
Protected areas in Greenland. The data are converted from the WFS that the ministery of mineral resources (MMR) in Greenland provides. Links are provided in the online resources.
-
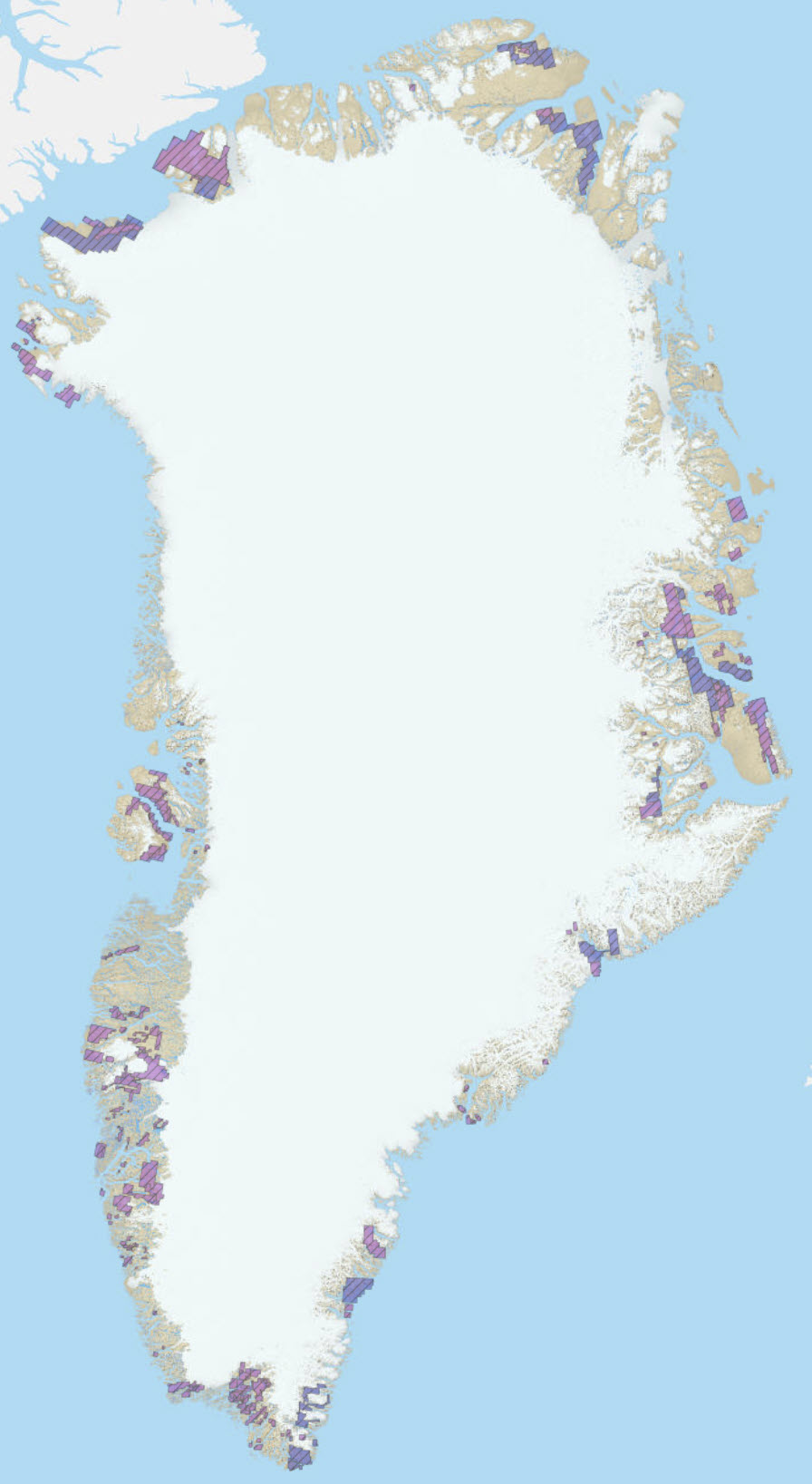
Historical mineral exploration and exploitation licences in Greenland. The data are converted from the WFS that the ministery of mineral resources (MMR) in Greenland provides. Links are provided in the online resources.
 Geus Geonetworks metadata catalogue
Geus Geonetworks metadata catalogue